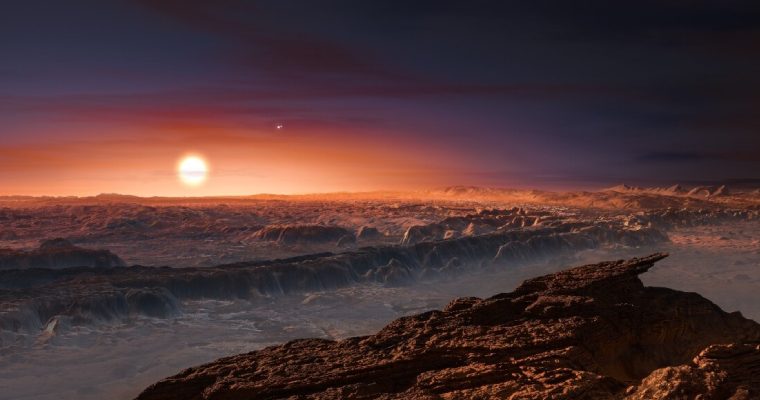
Located a mere 4.2 light-years away from Earth, an exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of its star has sparked intrigue due to its potential to sustain life. Proxima b, which boasts a mass only 1.3 times that of Earth and orbits a red dwarf star of similar age to our sun, has been the subject of ongoing investigations to determine its surface conditions.

Recent studies have presented conflicting views on Proxima b’s habitability, but a new research endeavor provides renewed hope. In a groundbreaking study published in the journal Astrobiology, scientists conducted climate simulations of Proxima b, incorporating a dynamic ocean.

As the planet is believed to be tidally locked, with a permanent dayside and nightside, static ocean models hinted at the possibility of a small dayside surface ocean despite limited sunlight. However, when a dynamic ocean was considered for the first time, the simulations revealed a much more significant presence of liquid water, with some regions extending into the nightside at low latitudes.
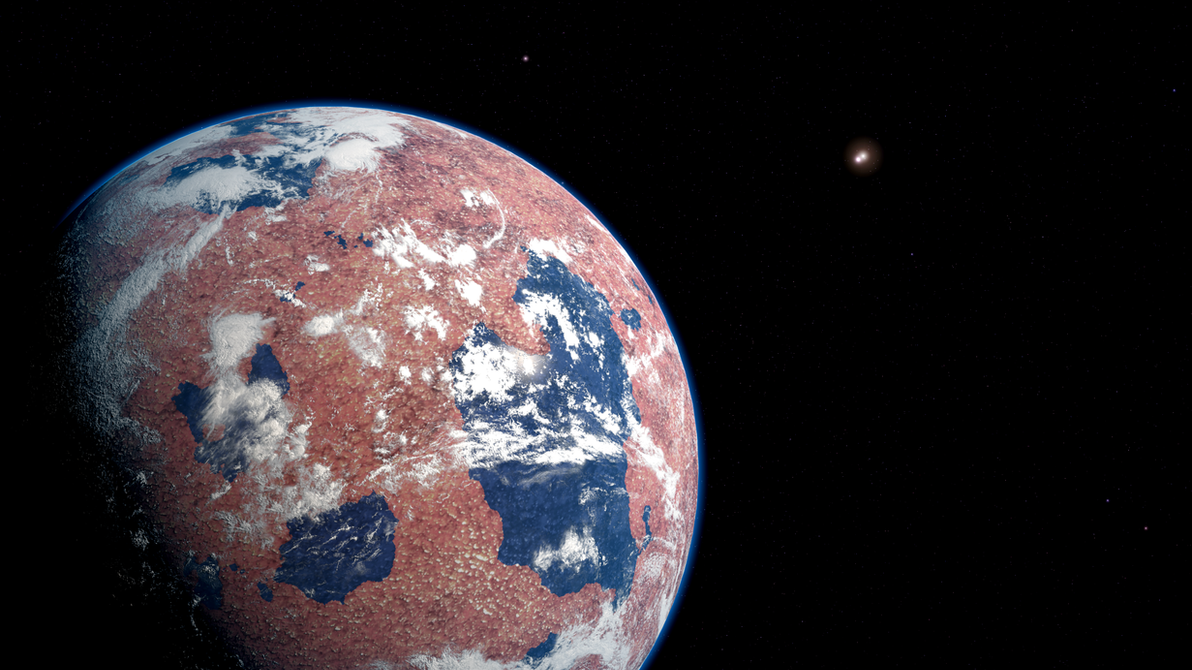

By exploring various factors such as salinity levels and atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations, the researchers identified the size of the liquid regions. Over a dozen simulations consistently demonstrated the existence of a liquid ocean on Proxima b. Nevertheless, it is crucial to note that the temperatures of these liquid areas would be significantly colder than previously anticipated, influenced by ocean heat transport and salinity-induced depression of the freezing point.

While the findings offer an intriguing glimpse into the potential habitability of Proxima b, further research and exploration are needed before we can dive deeper into the mysteries of this distant exoplanet.
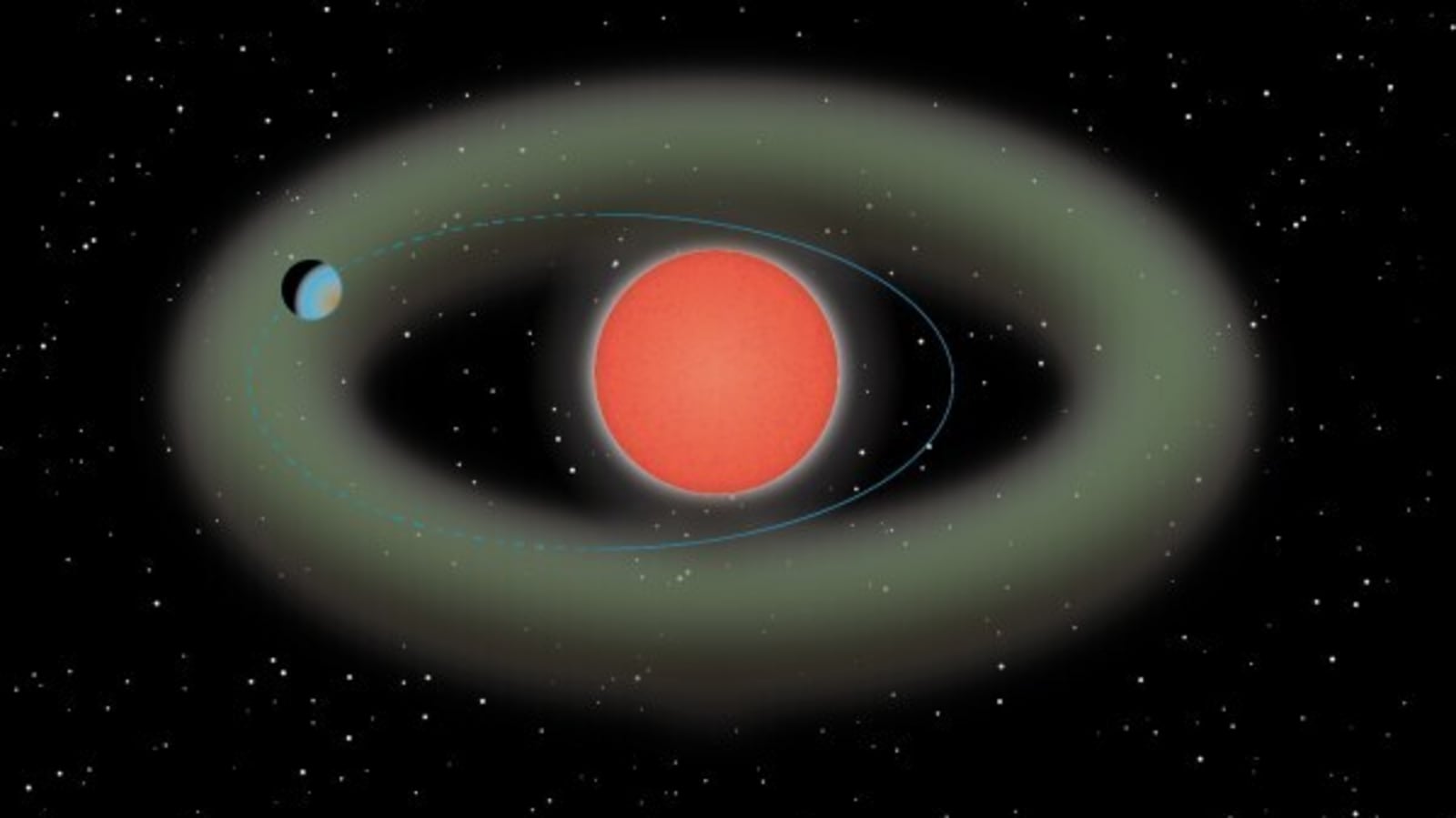
The discovery of this “Highly Likely” planet, situated just 4 light-years away, opens up a world of possibilities for further exploration and study. Astronomers can now focus their efforts on understanding the composition, atmosphere, and potential for life on this neighboring celestial body. This remarkable finding brings us one step closer to unraveling the mysteries of the universe and our place within it.